Description
The following outcomes are addressed in this pack:
ACMMG108 – Choose appropriate units of measurement for length, area, volume, capacity and mass
ACMMG109 – Calculate perimeter and area of rectangles using familiar metric units
ACMMG110 – Compare 12- and 24-hour time systems and convert between them
ACMMG111 – Connect three-dimensional objects with their nets and other two-dimensional representations
ACMMG113 – Use a grid reference system to describe locations. Describe routes using landmarks and directional language
ACMMG114 – Describe translations, reflections and rotations of two-dimensional shapes. Identify line and rotational symmetries
ACMMG115 – Apply the enlargement transformation to familiar two dimensional shapes and explore the properties of the resulting image compared with the original
ACMMG112 – Estimate, measure and compare angles using degrees. Construct angles using a protractor
Worksheets:
Page 1: Coversheet page with illustrations and spot to write name
Page 2: Appropriate Units of Measurement: Area & Capacity
Page 3: Appropriate Units of Measurement: Mass & Length
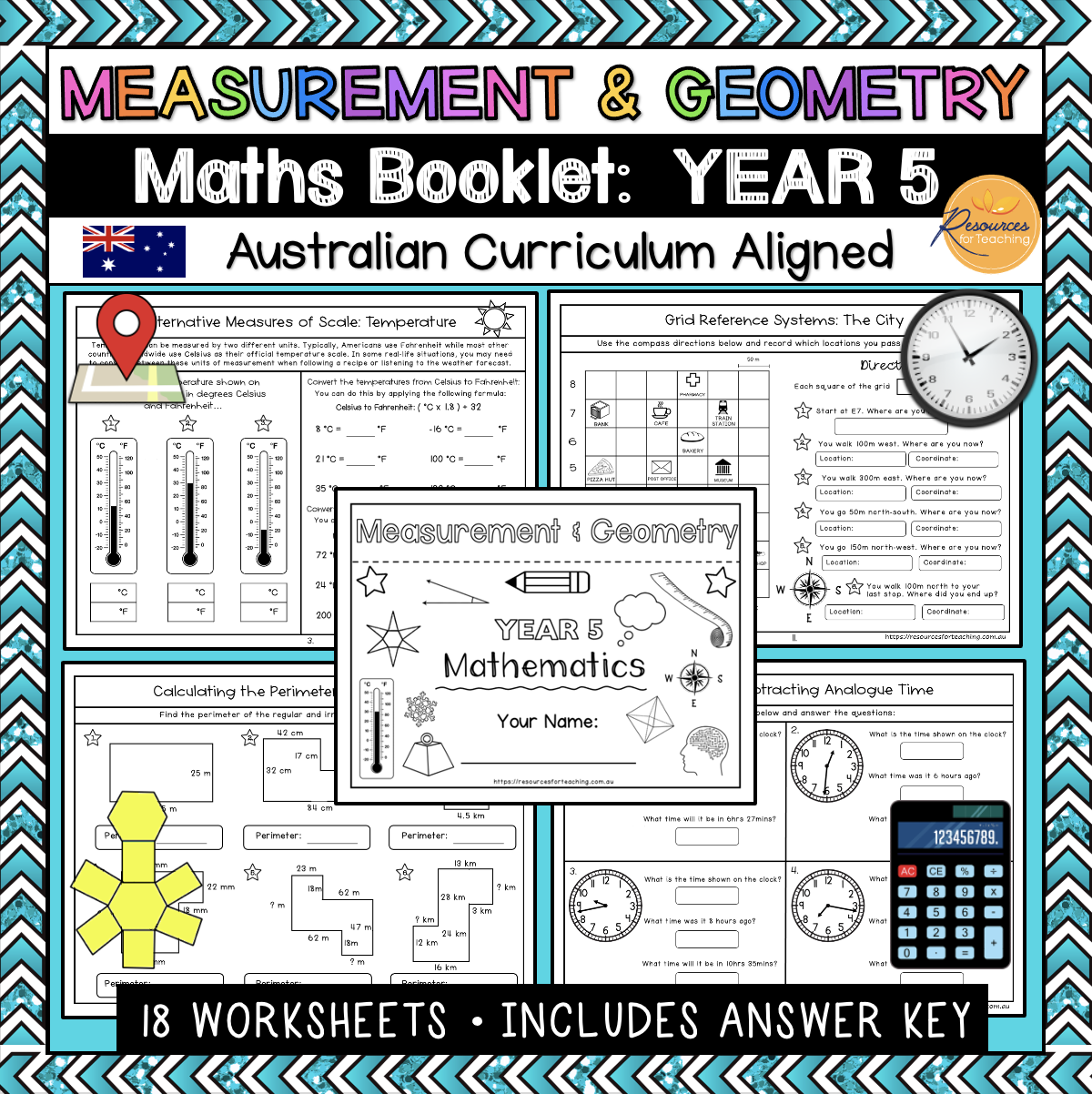
Page 4: Alternative Measures of Scale: Temperature (Degrees Celsius & Fahrenheit)
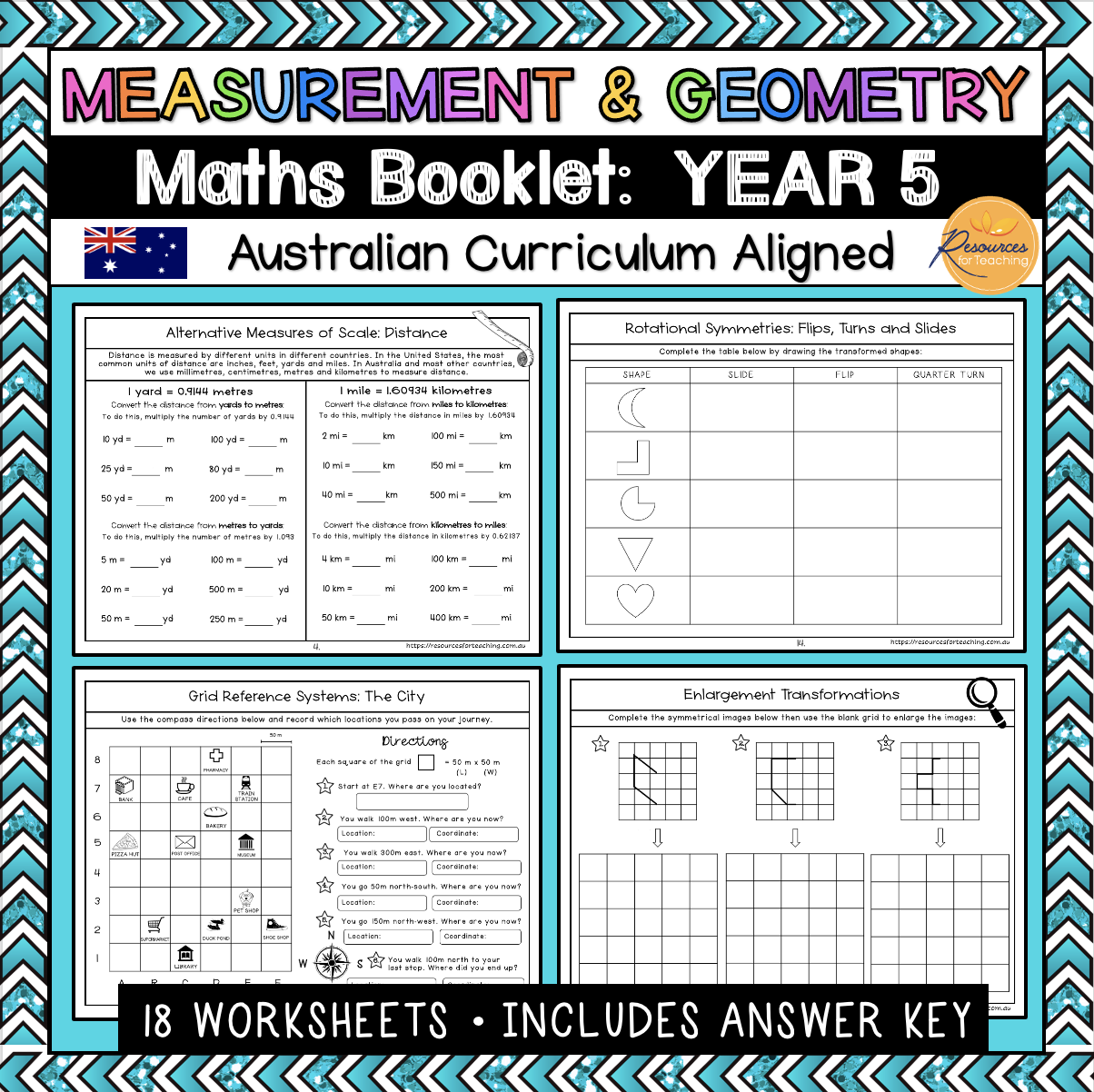
Page 5: Alternative Measures of Scale: Distance (Yards & Metres, Miles & Kilometres)
Page 6: Calculating the Perimeter of Rectangles
Page 7: Finding the Area of Rectangles
Page 8: 12- and 24-Hour Time Systems
Page 9: Adding and Subtracting Analogue Time
Page 10: 2D Nets and 3D Shapes
Page 11: Name the 2D Shapes
Page 12: Grid Reference System: The City
Page 13: Create Your Own Grid Reference System Template
Page 14: Translations, Reflections and Rotations
Page 15: Rotational Symmetries: Flips, Turns and Slides
Page 16: Enlargement Transformations
Page 17: Enlargements: Scale Factors
Page 18: Measuring and Classifying Angles
Page 19: Constructing Angles